Surface Water Vapour
 |
The humidity of air near the surface of the Earth affects the comfort and health of humans, livestock and wildlife, the swarming behaviour of insects and the occurrence of plant disease. The humidity near the surface affects evaporation and the strength of the hydrological and energy cycles. Evaporation from the surface of the earth is the source of water in the atmosphere and so is responsible for important feedbacks in the climate system due to clouds and radiation. |
|
| Domain: | Atmosphere | |
| Subdomain: | Surface | |
| Scientific Area: | Hydrosphere | |
| ECV Steward: | ||
| Products: | Dew Point Temperature (near Surface), Relative Humidity (near surface), Air Specific Humidity (near surface) | |
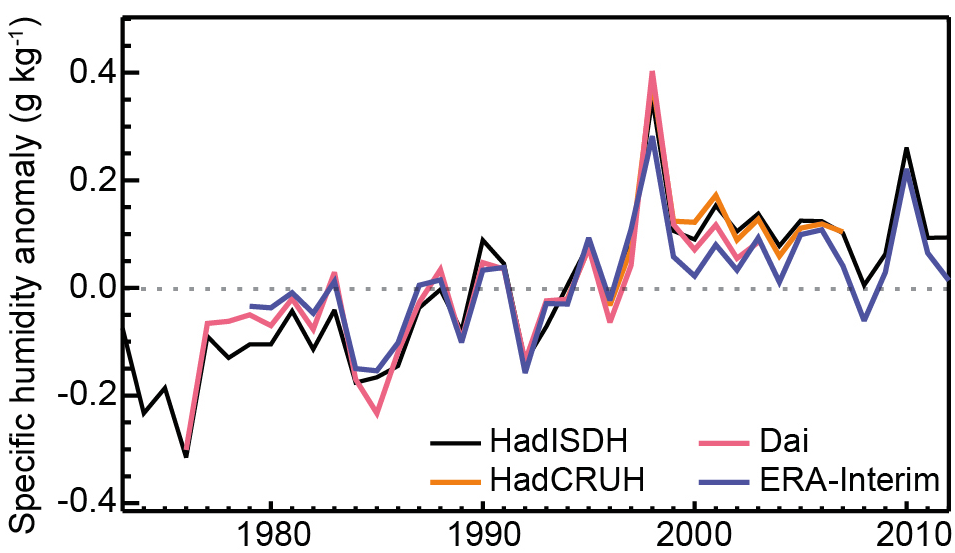
Global Surface Specific Humidity
|
Figure: Global annual average anomalies in land surface specific humidity from Dai (2006; red), HadCRUH (Willett et al., 2013; orange), HadISDH (Willett et al., 2013; black), and ERA-Interim (Simmons et al., 2010; blue). Anomalies are relative to the 1979-2003 climatology. Source: IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp, doi:10.1017/CBO9781107415324, Figure 2.30. |
ECV Products and Requirements
These products and requirements reflect the Implementation Plan 2022 (GCOS-244).
The requirements are found in the complete 2022 ECVs Requirements document as well: ECV Surface Water Vapour.
| Products | Dew Point Temperature (near Surface) | Relative Humidity (near surface) | Air Specific Humidity (near surface) | ||||||
| (*) | Unit | Values | Unit | Values | Unit | Values | |||
| Horizontal Resolution | G | km | 10 | km | 10 | km | 10 | ||
| B | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||||
| T | 500 | 500 | 500 | ||||||
| Vertical Resolution | G | - | - | - | |||||
| B | - | - | - | ||||||
| T | - | - | - | ||||||
| Temporal Resolution | G | h | <1 | h | <1 | h | <1 | ||
| B | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| T | 3 | 3 | 3 | ||||||
| Timeliness | G | h | 6 | h | 6 | h | 6 | ||
| B | 24 | 24 | 24 | ||||||
| T | 720 | 720 | 720 | ||||||
| Required Measurement Uncertainty (2-sigma) | G | K | 0.1 | %RH | 0.5 | g kg-1 | 0.1 | ||
| B | 0.5 | 2.5 | 0.5 | ||||||
| T | 1 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| Stability | G | K/decade | 0.01 | %RH/ decade | 0.05 | g kg-1/ decade | 0.01 | ||
| B | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.05 | ||||||
| T | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
(*) Goal (G): an ideal requirement above which further improvements are not necessary. Breakthrough (B): an intermediate level between threshold and goal which, if achieved, would result in a significant improvement for the targeted application. The breakthrough value may also indicate the level at which specified uses within climate monitoring become possible. It may be appropriate to have different breakthrough values for different uses. Threshold (T): the minimum requirement to be met to ensure that data are useful
Data Sources
This list provides sources for openly accessible data sets with worldwide coverage for which metadata is available. It is curated by the respective GCOS ECV Steward(s). The list does not claim to be complete. Anyone with a suitable dataset who wishes it to be added to this list should contact the GCOS Secretariat.
Gridded In Situ:
- HadCRUH – global marine and land surface humidity
- National Oceanography Centre Southampton (NOCS) Version 2.0 Surface Flux
In Situ:
- Integrated Surface Database (ISD) of the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- Hadley Centre Integrated Surface Database (HadISD)
- International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS)
Reanalysis:
- REANALYSES.ORG (Inventory for Reanalysis)