Fire


Average global annual Burned Area
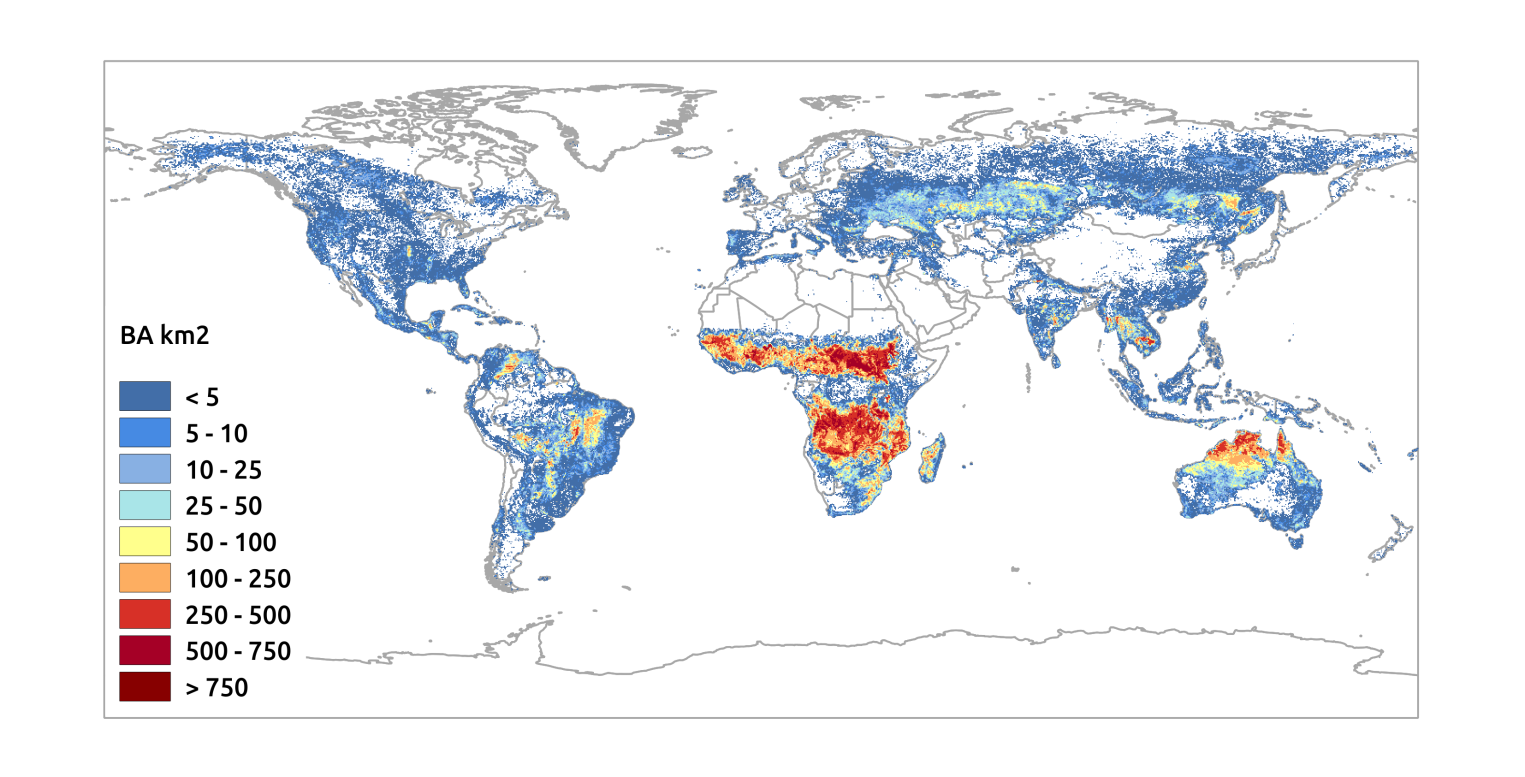
Figure: Average global annual Burned Area obtained from the FireCCI51 product for the period 2001-2017. Burned area detections were based on MODIS 250m near infrared reflectance and thermal anomalies (from Lizundia-Loiola et al., 2019, in review) |
ECV Products and Requirements
These products and requirements reflect the Implementation Plan 2022 (GCOS-244).
The requirements are found in the complete 2022 ECVs Requirements document as well: ECV Fire.
| Products | Burned Area | Active Fires | Fire Radiative Power (FRP) | ||||||
| (*) | Unit | Values | Unit | Values | Unit | Values | |||
| Horizontal Resolution | G | m | 10 | m | 50 | m | 50 | ||
| B | 100 | 250 | 250 | ||||||
| T | 1000 | 5000 | 5000 | ||||||
| Vertical Resolution | G | - | - | - | |||||
| B | - | - | - | ||||||
| T | - | - | - | ||||||
| Temporal Resolution | G | d | 1 | min | 5 | min | 5 | ||
| B | 10 | 120 | 120 | ||||||
| T | 30 | 720 | 720 | ||||||
| Timeliness | G | d | 10 | d | 1 | d | 1 | ||
| B | 120 | 7 | 7 | ||||||
| T | 360 | 365 | 365 | ||||||
| Required Measurement Uncertainty | G | % | 5 | % | 5 | MW km-2 of detector ground footprint | 0.5 | ||
| B | 15 | 5 | 1 | ||||||
| T | 25 | 5 | 2 | ||||||
| Stability | G | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | ||
| B | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| T | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||||||
(*) Goal (G): an ideal requirement above which further improvements are not necessary. Breakthrough (B): an intermediate level between threshold and goal which, if achieved, would result in a significant improvement for the targeted application. The breakthrough value may also indicate the level at which specified uses within climate monitoring become possible. It may be appropriate to have different breakthrough values for different uses. Threshold (T): the minimum requirement to be met to ensure that data are useful.
Data sources
Data Sources
This list provides sources for openly accessible data sets with worldwide coverage for which metadata is available. It is curated by the respective GCOS ECV Steward(s). The list does not claim to be complete. Anyone with a suitable dataset who wishes it to be added to this list should contact the abombelli wmo [dot] int (GCOS Secretariat).
wmo [dot] int (GCOS Secretariat).
- Satellite ECV Inventory by the CEOS/CGMS Working Group on Climate (WGClimate)
- Global burned area products generated under the Climate Change Initiative Programme of the European Space Agency
- Global burned area products generated by NASA